Robots have accompanied humans for decades now. They come in a variety of sizes, shapes and differ in how they work. Based on the design, industrial robots can be classified into 7 types: cartesian robots, cylindrical robots, scara robots, articulated robots, delta robots, polar robots, and collaborative robots (cobots).
In this article, we provide some overview information about commonly used robots in industry, as well as present their advantages, disadvantages, and applications in production.
What is an industrial robot?
The definition of an industrial robot
Industrial robots are automated machines designed to perform repetitive activities, tasks that require precision, heavy tasks, and replace humans in hazardous or harsh environments. They help reduce human errors and improve production productivity. Choosing the right type of robot to suit production requirements is an important key for manufacturing businesses.

Industrial robot
Structure of industrial robots
A typical industrial robot is composed of the following parts:
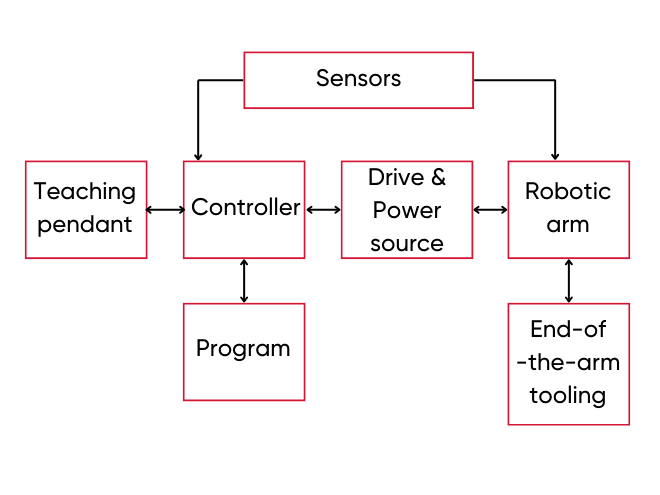
- Controller: this is considered the brain of the robot, which provides the robot with the memory and processing capabilities needed to operate.
- Sensors: Robots use sensors to perceive and collect data from the surrounding environment, these are the robot's ears and eyes.
- Drives and power sources: Robots can use electric, pneumatic, hydraulic, or other types of actuators to convert the energy needed for robot operations.
- Robotic arm: Designed to simulate a human arm, a robotic arm is a structure made up of many segments connected by joints/linkages. The joints can be linear joints, rotational joints, twisting joints, etc. They can be programmed to move as desired.
- End-of-arm tools (EOAT) or end effectors: They are customized equipment/actuators attached to the end of the robot arm to perform tasks. Some of the end-of-arm tools are grippers, cameras, welding heads, etc.
Different types of industrial robots
Nowadays there are many types of industrial robots for different applications, with their own strengths and weaknesses. This section will explain the working of some common types of industrial robots and list their advantages & disadvantages.
Cartesian robot
Cartesian robots, also known as gantry robots or Cartesian coordinate robots, are a type of industrial robot that performs linear movement in space (they move in a straight line, not in rotation). They move along the x, y, and z axes perpendicular to each other and form a cubic working area.
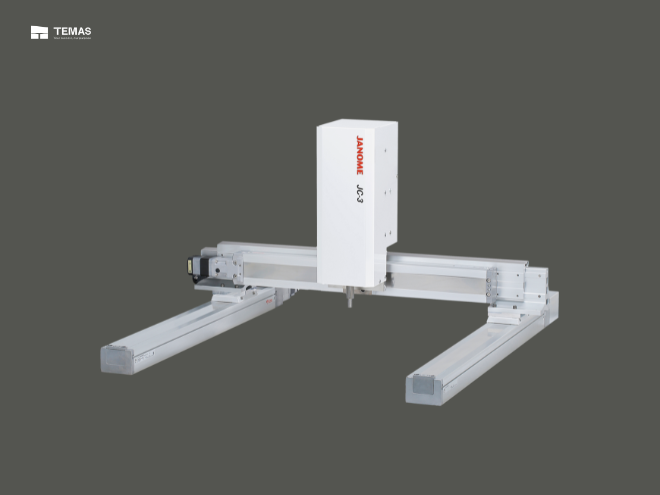

Janome Cartesian Robot
The Cartesian robot gets its name from the Cartesian coordinate system, which represents points in space as a function of the shortest distance from predetermined axes.
The drive system of a Cartesian robot can be belt drive, screw drive, cable drive or rack and pinion drive, or linear motors.
Advantages of Cartesian robots
- Simple design and operation: Cartesian robots have a simple design because they only move in 3 straight axes x, y, and z. Therefore, they can be easily configured, programmed, and operated.
- High precision: Thanks to its simple design, the Cartesian robot can be controlled accurately and easily. Their movements are highly precise, so they are often used in applications that require precision.
- Affordable price: Thanks to its simple design, the Cartesian robot can be controlled accurately and easily. Their movements are highly precise, so they are often used in applications that require precision.
Disadvantages of Cartesian robots
- Takes up space: Of all the industrial robots, the Cartesian robot is one of the most space-consuming. Operating along three straight axes x, y, and z, they need a cubic space to operate.
- Limited speed: Cartesian robots have slow speed, so they are not suitable for applications that require fast speed.
- Lack of flexibility: Because they only move in 3 straight, perpendicular axes, Cartesian robots are only suitable for the specific movements for which they are designed. Therefore they lack flexibility and are not suitable for complex applications.
- Easy to get contaminated: Because the structure of the Cartesian robot has many open mechanisms, the robot is easily contaminated, leading to parts being quickly worn and broken.
Application of Cartesian robot
Cartesian robots are often used in pick-and-place applications, packaging and inspection processes. They are also used in graphing, 3D printing, cutting and CNC applications.
Articulated robot
Articulated robots are industrial robots with joints that can rotate. Their joints are usually powered by servo motors and are called the robot's axes. The movements of the articulated robot are designed to simulate the movements of a human hand.
Usually, robots have 4 or 6 joints (4-axis robot, 6-axis robot), however in some more complex setups, robots can have up to 10 joints.)
Articulated robot
Advantages of articulated robots
- High flexibility: Articulated robots have many joints, allowing the robot to move flexibly, and reach more positions. They are suitable for applications that require flexibility.
- High speed: Articulated robots can achieve high speed, which improves productivity.
Disadvantages of articulated robots
- Complex: Articulated robots are designed to be relatively more complex than robots that only perform linear or horizontal rotation movements. Twisting joints require more parts and more careful consideration when manufacturing.
- Expensive: Because the structure of articulated robots is very complex, manufacturing and operating them is more difficult than simple robots, leading to high investment and maintenance costs.
Application of articulated robots
Because of their versatility, articulated robots are used in a wide variety of applications. They are especially suitable for applications that require dexterity and need to access a variety of positions such as coating, welding, painting, packaging,...
Cylindrical robot
A cylindrical robot is an industrial robot with a rotating joint in the base and a prismatic joint in the arm. The robot has three axes of motion, including two linear axes and one rotation axis. The axis connected to the base of the robot can rotate, and the arm can move up and down, and even expand to form a cylindrical workspace.
Advantages of cylindrical robots
- High load capacity: Cylindrical robots have high load capacity, and can easily carry heavy objects with their hands.
Disadvantages of cylindrical robots
- Takes up a lot of space: Cylindrical robots take up more floor space but do not offer many significant advantages, making them less popular compared to other industrial robots.
- Limitation in movement: Although a cylindrical robot can operate in a fairly large cylindrical workspace, it can only move objects from one plane to another without being able to overturn objects.
Application of cylindrical robots
Cylindrical robots are used in welding automation systems, material handling, assembly operations, painting and several other applications that require working with symmetrical circles.
Polar robot
A polar robot, or spherical robot, is a type of industrial robot with two rotating joints and one linear joint. The rotating joints are in charge of rotating and lifting the robot vertically. Linear joints help the robot expand its working area, allowing it to create a spherical workspace around itself.
These robots are named based on polar coordinates, a coordinate system in which each point in space is measured by its distance from the origin and the angle it makes with the axes about the origin. The polar robot is one of the first electrically powered robots that can move through space under complete computer control.
Advantages of polar robots
- Good lifting ability: Thanks to sturdy joints, the polar robot can lift objects with high loads.
Disadvantages of polar robots
- Takes up more space: Due to its bulky design, the polar robot does not optimize the available working space.
- Complex design: The polar robot has many joints with complex designs.
- High cost: Due to the complex design, the initial investment and operation and maintenance of polar robots are quite expensive.
Application of polar robots
Nowadays, polar robots are mostly replaced by articulated robots because they are more flexible and have superior performance, but some factories still use polar robots for injection molding, processing applications, materials handling, welding and some other common applications.
Delta Robot
Delta robots, also known as “spider robots”, are industrial robots designed with a triangular frame. The triangular frame is mounted directly above the work area, with each arm containing a high-torque servo motor.
The motor's shaft is connected to an arm called the "bicep", which extends in a direction perpendicular to the motor's axis of rotation. The other end of the biceps is connected to bars arranged in a parallelogram. Depending on the application, these parallelogram bars are connected to various manipulation tools.
Most of the weight of the spider robot is in the motor connected to the base, helping the parts move smoothly. Therefore, the moving parts have low inertia, can accelerate quickly and work at high speeds.
Advantages of delta robot/spider robot
- Fast speed, fast acceleration: Because the moving parts are lightweight bars, they move with low inertia, thereby helping the robot accelerate quickly and operate at high speed.
Disadvantages of delta robot/spider robot
- Cannot carry heavy load: Because the bars used to hold objects are quite thin and light, delta robots cannot carry heavy loads and are not suitable for applications that require high loads.
Application of delta robot/spider robot
Delta robots/spider robots are very suitable for applications that require quick placement of small products such as in the medical, pharmaceutical or food processing industries. They are also used in some packaging and welding processes.
SCARA robot
Robot SCARA stands for "Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm". As the name suggests, SCARA are special articulated robots that come with rotating joints. They can move mechanically in the x and y axes, moving fixedly in the z axis (up and down only).
Advantages of SCARA robot
- Good repeatability: SCARA is the robot with the best repeatability of all the articulated robots.
- Easy to install and save space: The SCARA robot has a swivel base, which can be easily mounted on a hard surface with a bracket. The robot's rack has a small area, helping to save installation space.
- High speed (with moderate load): Instead of hanging over the work area (like spider robots), SCARA robots have a base firmly attached to the work surface, giving them the ability to carry objects. Objects have heavier loads and better resistance. This allows them to work with heavy loads while still ensuring fast speeds.
Disadvantages of SCARA robot
- Suitable for applications requiring light to medium loads: SCARA robots are designed to carry objects with light to medium loads (about 10kg) to ensure fast speed and save space. Therefore, SCARA robots are not suitable for applications requiring high loads.
- Limited movement: Like cylindrical robots, SCARA robots cannot rotate and flip objects, so they have more limited movement.
Application of SCARA robot
The main application of SCARA robots is to pick and drop products at high speed and with high precision. They are versatile robots, often used for applications such as welding, engraving, material handling, etc.
Collaborative Robot (Cobot)
Collaborative robots, or cobots (Collaborative robots) are a type of industrial robot specifically designed to work in the same space with humans. These robots are capable of collaborating with humans on many tasks and at the same time doing automated work.
Because cobots work with humans, their most outstanding factor is their safety features. They use different types of sensors (force sensors, torque sensors, etc.) to determine human movements and ensure the safety of humans and other surrounding objects.
Some types of cobots are also designed to reduce speed and force when humans are nearby to ensure safety. However, cobots still ensure productivity and efficiency to working in harsh industrial environments.
With many joints, components and especially many safety and intelligent features, cobots are designed in a very complex way. Therefore, their cost is also significantly higher than that of conventional industrial robots, but they help improve working efficiency, especially when combined with humans.
Advantages of cobots
- Safety: Cobots are not only especially safe for humans but also safe for objects around them. Unlike other types of industrial robots that require iron frames or barriers, cobots with soft cushions and a variety of sensors will help ensure the safety of surrounding people and objects.
- Simplicity: Cobot has user-friendly software with a simple and friendly interface, even for people who do not have much experience with robots. They are designed to work collaboratively with humans, so even the programming is very easy and intuitive to make the collaboration process between humans and cobots more convenient.
- Flexibility: Thanks to the ease of setting up and reconfiguring a cobot, it is possible to easily switch between different operations or applications.
Disadvantages of cobots
- Limited speed: To ensure human safety, cobots often work at a limited speed even if they can accelerate even faster.
- High cost: Due to its complex structure and many safety features, cobots often have a high initial investment cost.
- Requires multiple approvals: Countries around the world have different rules to ensure collaborative robots are absolutely safe for humans to work with. Therefore, building a collaborative working system between humans and cobots in the factory will require many safety factors and necessary licenses.
Application of cobots
Cobots can be used in many applications due to their flexibility of movement, simple reconfiguration, and ability to collaborate with humans. Common industrial applications of cobots include screw driving, polishing, sealing, pick-and-place, etc. In addition, cobots are also known for real-life applications such as demonstrations, sales, service, medical support,... things that other industrial robots cannot do.
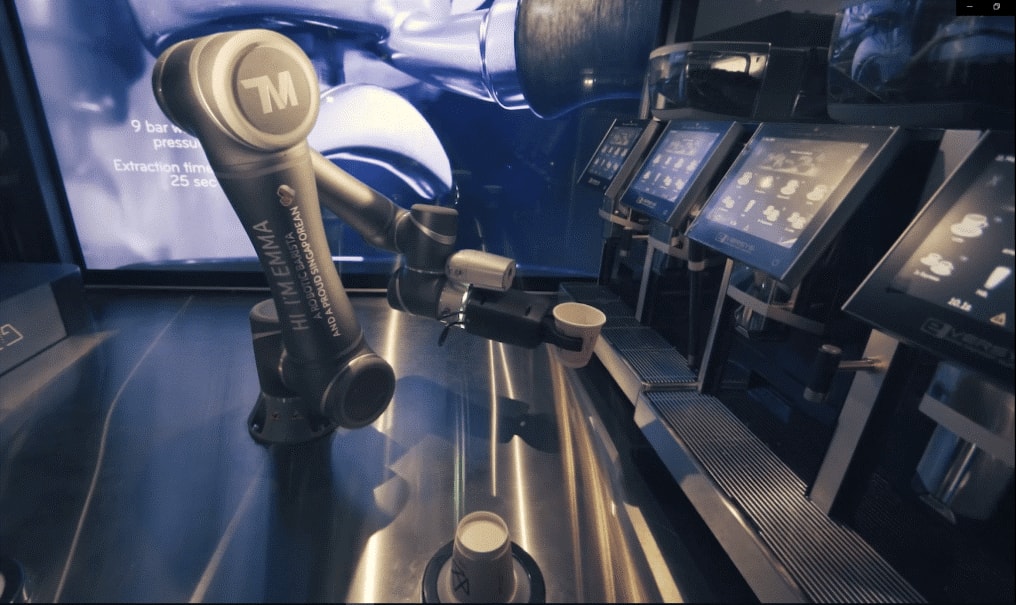

A cobot is serving coffee at a coffee shop in Singapore
Summary: Compare types of industrial robots
| Robot type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Appplication |
| Cartesian Robot |
|
|
Pick-and-place, packaging and inspection processes, graphing, 3D printing, cutting and CNC applications, etc. |
| Articulated Robot |
|
|
Applications that require dexterity and need to access a variety of positions such as coating, welding, painting, packaging, etc. |
| Cylindrical Robot |
|
|
Welding automation systems, material handling, assembly operations, painting, etc. Other applications that require working with symmetrical circles. |
| Polar Robot |
|
|
Injection molding, processing applications, materials handling, welding and some other common applications. |
| Delta Robot |
|
|
Applications that require quick placement of small products such as in the medical, pharmaceutical or food processing industries. They are also used in some packaging and welding processes. |
| SCARA Robot |
|
|
Pick and place products at high speed and with high precision such as welding, engraving, material handling, etc. |
| Collaboration Robot (cobot) |
|
|
Screw driving, polishing, sealing, pick-and-place, etc. Real-life applications such as demonstrations, sales, service, medical support, etc. |
Temas has presented the definition of industrial robots, their classification and their applications. Temas distributes industrial robots: Techman collaborative robot, Cartesian Janome robot, Epson SCARA robot,... See more about the list of robots we distribute here.


 Read more
Read more



