Industry 4.0 has long been a familiar concept to automation engineers. Recently, a new term, "Industry 5.0" has emerged. So, what exactly is Industry 5.0, and how does it differ from Industry 4.0?
Industry 5.0 is one of the most exciting trends of 2025. It represents the next phase in the evolution of manufacturing, where advanced technologies such as AI and robotics integrate with human creativity and sustainability.
In this article, we will explore the key differences between Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0, examine the technologies driving this transition, and analyze how it will transform industries worldwide.
Key Differences Between Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0
The transition from Industry 4.0 to Industry 5.0 marks a significant shift in manufacturing. While Industry 4.0 primarily focuses on automation and efficiency, Industry 5.0 emphasizes human-centric solutions and sustainability. This shift reflects a growing recognition of the importance of human well-being and environmental responsibility in industrial production.
One key distinctions between Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0 is the role of human involvement in production. Industry 5.0 promotes collaboration between human workers and smart machines, enhancing both productivity and job satisfaction. This approach not only improves manufacturing efficiency but also fosters a more creative and engaged workforce.
Building on the digital foundation of Industry 4.0, Industry 5.0 integrates empathy, creativity, and ecological awareness. The result is an industrial ecosystem that values connectivity and optimization while prioritizing human well-being and environmental sustainability. This integrated approach helps organizations adapt to evolving regulations, consumer expectations, and resource constraints.
| Industry 4.0 vs. Industry 5.0 | ||
| Aspect | Industry 4.0 | Industry 5.0 |
| Focus | Automation and efficiency | Human-centric design and sustainability |
| Role of Humans | Limited to supervisory roles | Central to collaboration and creativity |
| Use of Technology | Data-driven automation | AI-enhanced human-machine interation |
| Sustainability | Secondary focus | Primary objective |
Core Principles of Industry 5.0
At its core, Industry 5.0 adopts a human-centric approach, integrating human values into industrial production. It aims to create a more personalized and empathetic work environment, emphasizing the value of human labor.
This approach not only enhances job satisfaction but also fosters creativity and critical thinking—key drivers of innovation in manufacturing. Let’s explore the core principles of Industry 5.0 to better understand how it differs from Industry 4.0.
1. Principle 1: Human-Centric Design
Human-centric design is the foundation of Industry 5.0, ensuring that technology supports rather than replaces human roles in industrial processes. This approach prioritizes worker needs and benefits, creating a more intuitive and engaging work environment that values human contributions.
Human-centric design is the foundation of Industry 5.0
By leveraging cognitive computing and systems engineering, Industry 5.0 fosters workplaces where humans and machines collaborate seamlessly. Key aspects include:
- Seamless Human-Machine Interaction: Robots and AI handle repetitive and mundane tasks, allowing workers to focus on creativity and critical thinking. Advanced technologies like sensors, actuators, and machine learning enable robots to work alongside humans, improving productivity and job satisfaction.
Techman collaborative robots work alongside humans in welding applications
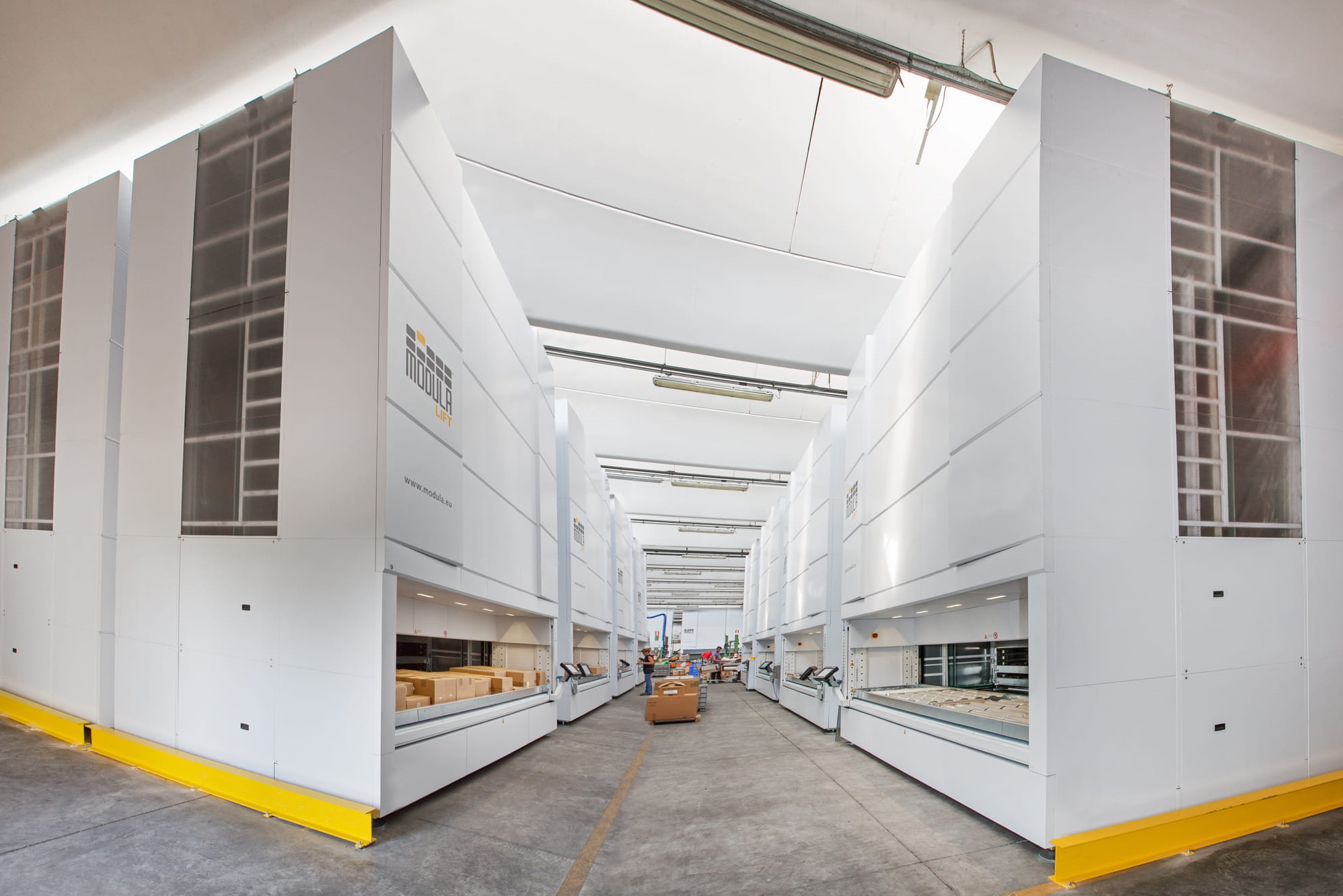
- Ergonomic Work Environments: Manufacturing processes are designed with ergonomics in mind, enhancing employee well-being and work efficiency.
The Modula Smart Warehouse - an example of a technology-driven warehouse solution with ergonomic design
- Ethical Leadership: Businesses incorporate empathy into their strategies—actively listening to and respecting employee input—which leads to long-term benefits such as increased job satisfaction, loyalty, and better business performance.
For businesses transitioning to Industry 5.0, adopting human-centric values is essential. This approach also positively impacts customer satisfaction by ensuring a motivated workforce delivers their best work.
2. Principle 2: Sustainability
Sustainability is a fundamental principle of Industry 5.0, focusing on reducing the environmental impact of industrial production by adopting sustainable practices and minimizing waste. By integrating advanced technologies, Industry 5.0 fosters a more resource-efficient and environmentally friendly industry.
Sustainability will become a mandatory requirement in the future to enhance competitiveness.
Key Strategies for Sustainability:
- Circular Economy Practices: Recycling and reusing materials extend product lifecycles, emphasizing resource conservation and waste reduction.
- Energy Management: Smart machinery and energy-efficient technologies minimize energy waste, improving production efficiency while reducing environmental impact.
- Resource Optimization: AI and machine learning optimize processes, reducing waste and enhancing energy efficiency.
Industry 5.0 is committed not only to improving production efficiency but also to contributing to planetary health. These practices help conserve resources while ensuring industrial growth aligns with environmental responsibility, paving the way for a sustainable future.
3. Principle 3: Seamless Collaboration
The transition to Industry 5.0 is driven by a range of advanced technologies that enable seamless collaboration between humans and machines.
Key Enabling Technologies:
- Cloud Computing: Used by 94% of global enterprises, cloud computing allows manufacturers to predict equipment failures, optimize production processes, and monitor operations in real time. The global cloud computing market is expected to grow from $445.3 billion in 2021 to $947.3 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.3% (Source: Zippia).
- Big Data Analysis: Big data analytics is a major driver of innovation in manufacturing, enabling advanced algorithms to optimize production quality and operational efficiency. The global big data market in manufacturing is expected to expand from $3.22 billion in 2018 to $21.51 billion by 2032, with a CAGR of 12.6% (Source: Fortune Business Insights).
- Blockchain: Ensures data security and transparency, particularly in supply chain management, reducing fraud and enhancing trust. Blockchain plays a crucial role in improving transparency, security, and efficiency in manufacturing supply chain management (Source: LA Blockchain Summit).
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT enables smart factories to enhance energy efficiency and optimize production processes. For instance, Bosch’s IoT Energy Platform has helped its flagship factory in Homburg, Germany, reduce carbon emissions by 12% while improving overall energy efficiency.
- 6G Network: Although still in the development phase, 6G promises data transmission speeds 100 times faster than 5G, enabling unprecedented real-time communication and control. It is expected to deliver data transfer speeds of up to 1,000 gigabits per second (Source: TT Consultants).
These technologies collectively support the creation of smart factories, where production processes are optimized in real-time, enhancing both efficiency and sustainability. They also create a competitive advantage by seamlessly integrating human and machine capabilities, driving adaptability in the manufacturing sector.
Applications of Industry 5.0
Industry 5.0 is revolutionizing industries by combining advanced technologies with human-centric solutions, enhancing customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. Some key applications of Industry 5.0 include:
- Smart Manufacturing: Industry 5.0 integrates digital twin systems, AI, and collaborative robots (cobots) to improve production efficiency and responsiveness. Real-time monitoring and simulation systems optimize operations, adjust processes based on customer needs, and reduce waste. These innovations create sustainable and adaptive production lines, meeting both environmental and market demands.
Collaborative robots, equipped with machine vision and real-time control systems
- Healthcare Innovation: By integrating human insights and expertise into workflows, Industry 5.0 ensures personalized, efficient, and responsive healthcare systems that cater to patient needs.
- Sustainable Supply Chains: Advanced technologies like cobots, blockchain, and big data analytics are transforming supply chains. Blockchain enhances transparency and security, while AI-driven data analytics forecasts demand and optimizes resources. These innovations minimize risks, waste, and environmental impact, creating sustainable supply chains.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its benefits, transitioning to Industry 5.0 poses several challenges, such as security concerns, skill gaps, lengthy processes, and significant budget requirements. However, to remain competitive, manufacturers must prioritize sustainability, collaboration, and workforce upskilling. Below are some tips to overcome these challenges.
Skill Gap
Addressing the skill gap is crucial for adopting Industry 5.0. Proper training enables employees to effectively collaborate with advanced technologies like AI and cobots. Continuous learning fosters effective human-machine collaboration, boosting productivity and innovation.
Tip: Invest in visual training tools and collaborate with educational institutions to ensure your workforce is future-ready
Addressing Security Concerns
As connected technologies enhance operational efficiency, they also increase cybersecurity risks.
Manufacturers must proactively adopt data protection measures, such as regular assessments, data updates, and employee training. Robust security strategies ensure resilience against threats, safeguarding both systems and valuable data assets.
Tip: Establish a security roadmap and ensure all employees are trained to recognize threats..
Exploring Future Technologies
Preparation and research into future technologies are essential. Industry 5.0 focuses on advanced technologies like AI, digital twins, and quantum computing, enabling real-time decision-making, accurate simulations, and improved efficiency.
Another priority is enhancing human-machine interaction, fostering intuitive work environments that boost productivity and job satisfaction.
Continuous innovation and exploration of emerging technologies are vital for creating a sustainable, adaptive, and resilient manufacturing industry that meets the evolving needs of workers and customers.
Tip: Allocate R&D resources to assess how emerging technologies align with your business goals..
Industry 5.0 marks a significant leap in manufacturing, emphasizing human-centric design, sustainability, and advanced technologies. By integrating AI and collaborative robots, it enhances productivity while prioritizing worker well-being and environmental safety in modern production.
At Temas, we pursue a sustainability-driven operational philosophy, with a team of experienced automation engineers delivering turnkey solutions that align with Industry 5.0 trends. Contact us today to upgrade your manufacturing facility

 Read more
Read more